A Climate Crisis That Threatens Millions
The American West is facing a water crisis that is having devastating and lasting effects on the environment, economy and society. The region is experiencing its worst megadrought in at least 1,200 years, according to a new study published in Nature Climate Change.
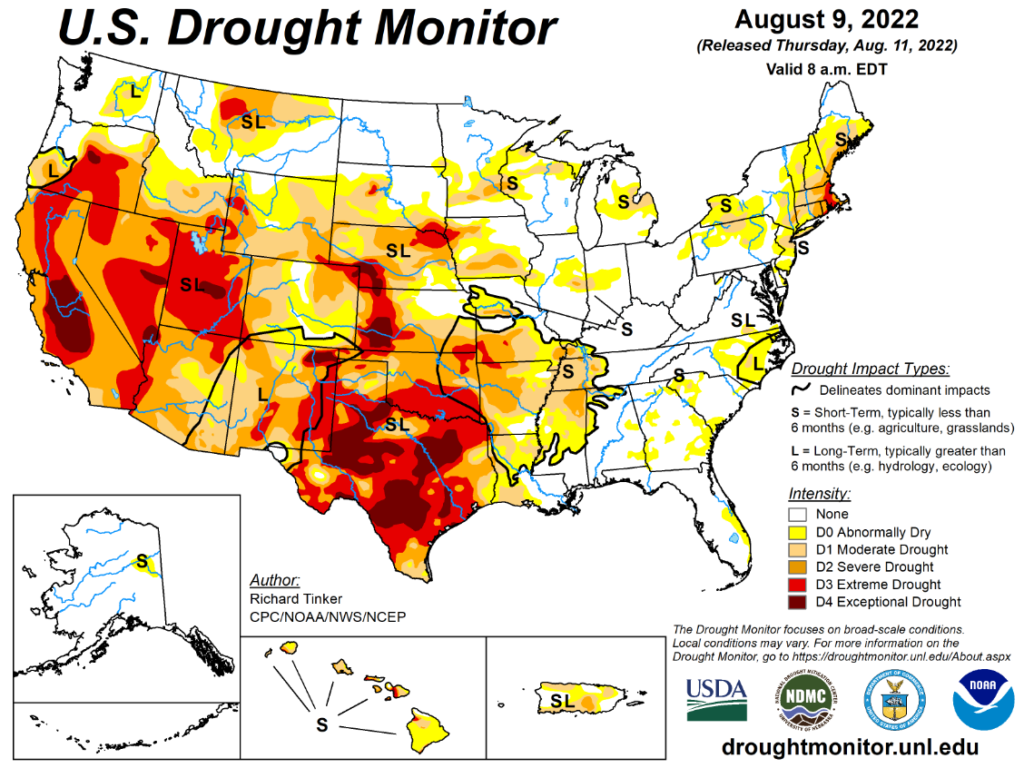
Climate change is exacerbating this condition not only in the US, but world-wide with drought impacting food and water security in South America, Europe, Asia and the African continent.
What is a Megadrought?
A megadrought is a severe and prolonged drought that lasts for two decades or more. The current megadrought, which began in 2000, has reduced water supplies, damaged crops, caused water shortages, lowered the water level of reservoirs and lakes, and fueled wildfires across the region.
What causes a megadrought?
The main factors are natural variability in precipitation and temperature, which can affect the amount and timing of rainfall and snowfall, as well as the evaporation and transpiration of water from the soil and plants.
However, human-induced climate change is also playing a major role in making the current megadrought so extreme. The study found that climate change was responsible for about 40% of the severity of the current megadrought, and that it prevented a wet year in 2005 from ending the drought event.
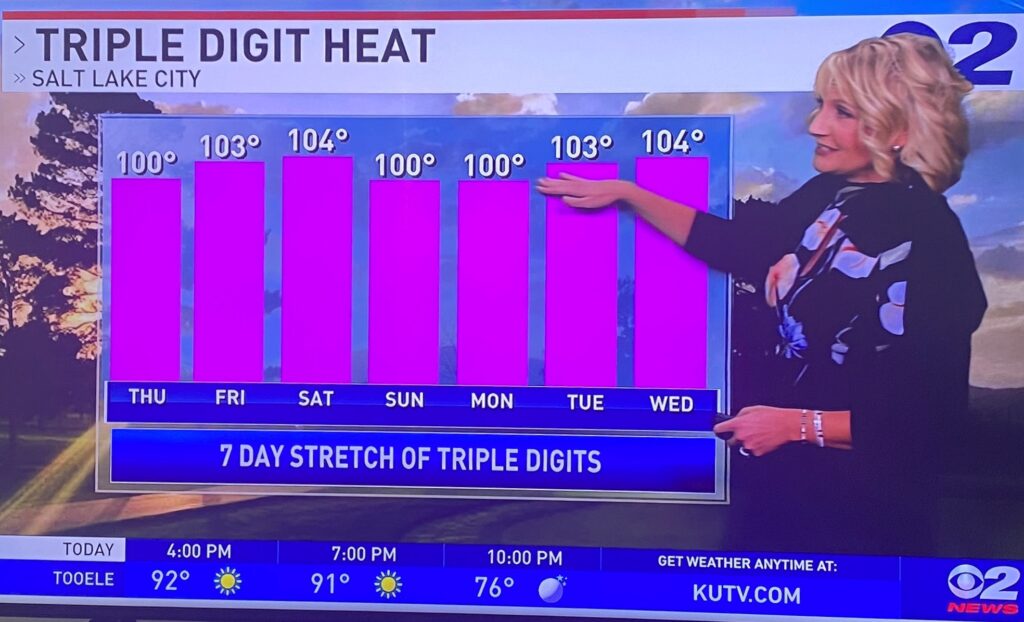
Climate change is increasing the frequency and intensity of heat waves, which dry out the soil and vegetation, and reduce the snowpack that feeds rivers and streams.
What are the consequences of a megadrought?
The impacts of a megadrought are far-reaching and long-lasting. They affect not only the natural ecosystems, but also the human systems that depend on water for agriculture, energy, industry and recreation. Some of the consequences include:
- Reduced crop yields and livestock production, leading to higher food prices and food insecurity.
- Decreased water availability and quality, leading to water restrictions, conflicts and health risks.
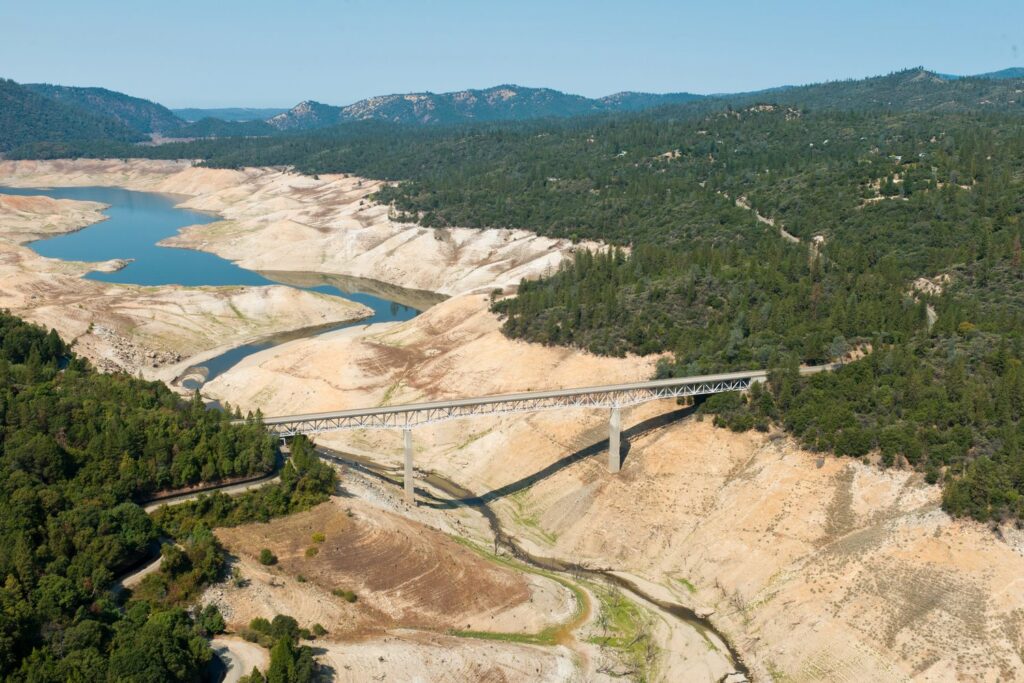

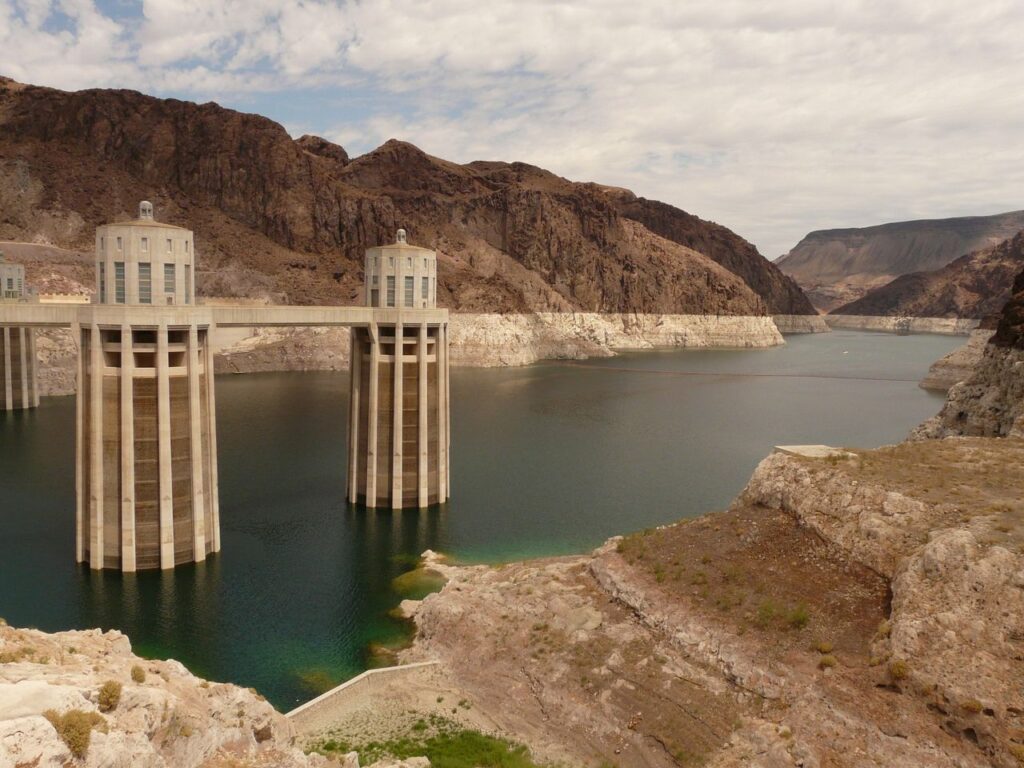
- Lowered water levels in reservoirs and lakes, affecting hydropower generation, navigation, recreation and wildlife habitat.

- Increased risk of wildfires, which can destroy homes, infrastructure, forests and wildlife, and worsen air quality and public health.

- Altered ecosystems and biodiversity, which can affect the services they provide such as pollination, pest control, carbon sequestration and soil fertility.
How can we cope with a megadrought?
There is no easy solution to a megadrought. It requires a combination of adaptation and mitigation strategies that involve multiple stakeholders at different scales. Some of the possible actions include:
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions to limit global warming and its effects on droughts.
- Improving water management and conservation practices to use water more efficiently and equitably.
- Investing in water infrastructure and technology to enhance water storage, distribution and treatment.
- Promoting drought-resilient agriculture and forestry to reduce water demand and increase productivity.
- Enhancing drought monitoring and forecasting to improve preparedness and response.
- Supporting drought-affected communities and ecosystems to recover and adapt.
What can I do to prepare?
Back in June I wrote about the need for having a supply of water stored. In July I talked about having a way to filter water in an emergency. Click the links to read those articles.
Where can I learn more?
Conclusion
The Western megadrought is a climate crisis that threatens millions of people and countless species. It is a wake-up call for us to act now to reduce our greenhouse gas emissions and manage our water resources more sustainably. The future of the West depends on it.
Last Updated on September 1, 2022